Does Televised Aggression Research Consider The Monster Effect?
Are you curious about how televised violence might shape our behavior, especially when it comes to the fantastical realms of monsters and mayhem? At monstertelevision.com, we delve deep into this topic, exploring the chilling effects of televised aggression, unpacking the psychological impact, and offering insights into mitigating potential risks. Let’s explore the captivating connection between televised aggression research and the impact of monster-themed content, offering you practical advice for navigating the world of monster television responsibly. Join us as we uncover the science behind the screen and discover how to enjoy your favorite monster shows while minimizing any negative influences with educational content.
1. What Does The Text Consider Research On Televised Aggression As?
The Text Considers Research On Televised Aggression As a significant area of study demonstrating a link between exposure to violence in media and an increased risk of aggressive behavior. It acknowledges that numerous studies, including research from the University of Southern California School of Cinematic Arts, suggest a correlation between viewing violent content and subsequent aggressive tendencies. It’s not just about monsters, zombies, or aliens battling it out on screen; it’s about understanding how these portrayals impact our actions and attitudes.
1.1 How Does Research Define Media Violence?
Media violence, as defined by researchers, typically refers to the visual depiction of physical aggression by one character (human or human-like) against another. This definition has evolved alongside theories about the effects of media violence, aiming to pinpoint the kind of violent content most likely to teach viewers, particularly children, to be more aggressive. It encompasses a wide range of portrayals, from classic monster movies to modern video games, all of which contribute to the ongoing debate about the impact of violent media on society.
1.2 What Types Of Media Are Included In This Definition?
This definition includes television programs, movies, video games, internet content, and even cell phone displays. This broad inclusion recognizes that violence can be portrayed across various platforms, each with its own unique way of influencing viewers. For instance, the immersive nature of video games may have a different effect compared to passively watching a movie. Each medium contributes to the ongoing discussion about the impact of violent content on society.
1.3 How Does This Differ From Public Perception?
While the public may have varying perceptions of what constitutes media violence, researchers maintain a clear definition to ensure consistency and accuracy in their studies. Laypersons might focus solely on graphic depictions of violence, while researchers consider the broader context, including the motivations behind the violence and the potential for viewers to internalize aggressive behaviors. This difference highlights the importance of scientific rigor in understanding the true impact of media violence.
1.4 What Is Considered Aggressive Behavior By Researchers?
Researchers define aggressive behavior as any action intended to harm or irritate another person. This definition encompasses both physical and non-physical aggression, including insults, spreading rumors, and, of course, physical violence. It’s important to note that aggression, in this context, is distinct from assertiveness, which lacks the intent to harm. Understanding this distinction is crucial for accurately assessing the impact of media violence on real-world behavior.
1.5 What Actions Are Considered Violent Behavior?
Violent behavior specifically refers to more serious forms of physical aggression that carry a significant risk of seriously injuring the victim. This includes actions such as pushing, shoving, fighting, serious assaults, and homicide. These are the behaviors of greatest concern in the study of media violence, as they have the most severe consequences for both individuals and society.
1.6 What Factors Contribute To Violent Or Aggressive Actions?
Violent or aggressive actions seldom result from a single cause. Rather, multiple factors converging over time contribute to such behavior. The influence of violent mass media is best viewed as one of the many potential factors that influence the risk for violence and aggression. No reputable researcher is suggesting that media violence is “the” cause of violent behavior. A developmental perspective is essential for an adequate understanding of how media violence affects youthful conduct and in order to formulate a coherent response to this problem.
2. What Psychological Theories Explain The Detrimental Effects Of Exposure To Violence?
Psychological theories attribute the detrimental effects of exposure to violence to short-term processes like priming, arousal, and mimicry, as well as long-term effects such as observational learning and desensitization. These theories, explored further at monstertelevision.com, explain how viewing violence can alter our thoughts, emotions, and behaviors, leading to an increased risk of aggression. Understanding these mechanisms is key to mitigating the potential negative impact of violent content.
2.1 How Does Priming Influence Aggressive Behavior?
Priming is a process where exposure to a stimulus activates associated concepts in the brain, making related behaviors more likely. For example, seeing a gun can prime aggressive thoughts and behaviors. Media violence can prime aggressive concepts, leading to an increased likelihood of aggression. This effect is particularly concerning because it can occur subconsciously, influencing behavior without conscious awareness.
2.2 What Role Does Arousal Play In Short-Term Aggression?
Arousal from media violence can lead to increased aggression through excitation transfer and general arousal. Excitation transfer occurs when arousal from the media presentation is misattributed to a subsequent provocation, making the provocation seem more severe. Increased general arousal can also diminish inhibitions, leading to the display of dominant, learned responses, such as direct instrumental aggression. This means that even if the viewer isn’t inherently aggressive, the heightened emotional state induced by violent content can make them more prone to act out.
2.3 Can Mimicry Of Observed Behaviors Lead To Violent Tendencies?
Yes, mimicry, or imitation of specific behaviors, can lead to violent tendencies, especially in children. Research suggests that humans have an innate tendency to mimic observed behaviors. When children observe violent behavior, they are more likely to mimic it. Mirror neurons, which fire when a behavior is observed or acted out, may play a crucial role in this process. This highlights the importance of monitoring the types of behaviors children are exposed to, as they are more likely to internalize and replicate them.
2.4 How Does Observational Learning Contribute To Long-Term Effects?
Observational learning involves encoding social scripts through observation of family, peers, community, and mass media. Over time, children develop social cognitive schemas about the world around them. Extensive observation of violence can bias children’s world schemas toward attributing hostility to others’ actions, increasing the likelihood of aggressive behavior. These learned behaviors can become ingrained over time, making them difficult to change.
2.5 What Is Desensitization, And How Does It Impact Emotional Responses?
Desensitization is the process by which repeated exposure to emotionally activating media can lead to a habituation of certain natural emotional reactions. Negative emotions experienced in response to violent or gory scenes decline in intensity after many exposures. This can lead to a blunted emotional response and a greater tolerance for violence. Desensitization can be particularly concerning because it may reduce empathy and increase the likelihood of engaging in or condoning violence.
2.6 What Is Enactive Learning And How Does It Affect Behavior?
Enactive learning occurs when individuals are not just observers but active participants in violent actions, such as in video games. The reinforcement gained for using violence to achieve goals can lead to long-term increases in violent behavior. This active participation can have a greater impact than passively watching violence in TV or movies. The interactive nature of video games, coupled with the reward system, can create a powerful learning environment that promotes aggressive behavior.
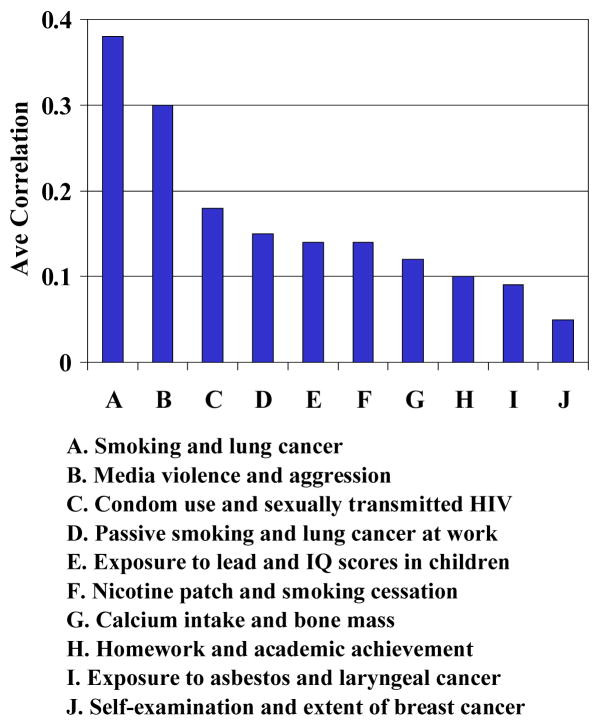
3. How Does The Size Of The “Media Violence Effect” Compare To Other Societal Threats?
The “media violence effect” is comparable to other well-known threats to public health, such as smoking, highlighting the significant impact of media violence on society. According to research from Bushman and Huesmann at the University of Southern California School of Cinematic Arts, the effect size of media violence on aggression is similar to or larger than the effect size of many other recognized public health threats. This suggests that media violence should be taken seriously as a potential risk factor for violent behavior.
3.1 What Evidence Supports The Claim That Media Violence Is A Significant Threat?
Meta-analyses, which average the effects observed in many studies, provide the best overall estimates of the effects of media violence. These analyses have revealed effect sizes for violent video games ranging from .15 to .30. Specifically, playing violent video games has been linked to increases in aggressive behavior, aggressive affect, aggressive cognitions, physiological arousal, and decreases in prosocial behavior. These findings suggest that media violence has a significant and measurable impact on behavior.
3.2 How Do Meta-Analyses Help In Assessing The Effects Of Media Violence?
Meta-analyses provide a comprehensive summary of the research by combining data from multiple studies. This allows researchers to obtain a more precise estimate of the overall effect of media violence. By averaging the results of many studies, meta-analyses can reduce the impact of individual study biases and provide a more reliable assessment of the relationship between media violence and aggression.
3.3 What Is The File Drawer Effect, And How Is It Addressed In Research?
The file drawer effect refers to the fact that studies with non-significant results are less likely to be published and appear in meta-analyses. This can lead to an overestimation of the true effect of media violence. To address this problem, researchers estimate how many null-effect studies it would take to change the results of the meta-analysis. This helps to determine the robustness of the findings and ensures that the conclusions are not solely based on published studies.
3.4 Can You Provide Examples Of Meta-Analyses On The Effects Of Media Violence?
Two notable meta-analyses are those of Paik and Comstock, which focused on violent TV and films, and Anderson and Bushman, which focused on violent video games. Paik and Comstock examined effect sizes from 217 studies published between 1957 and 1990 and found an average effect size of r =.38 for randomized experiments. Anderson and Bushman’s meta-analyses revealed effect sizes for violent video games ranging from .15 to .30.
3.5 Are Experiments Able To Test The Effects Of Media Violence?
Experiments unambiguously show that viewing violent videos, films, cartoons, or TV dramas, or playing violent video games, causes the risk to go up that the observing child will behave seriously aggressively toward others immediately afterwards. This is true of preschoolers, elementary school children, high school children, college students, and adults. Those who watch the violent clips tend to behave more aggressively than those who view non-violent clips, and they adopt beliefs that are more “accepting” of violence.
3.6 What Is The Significance Of Longitudinal Studies In Understanding Media Violence Effects?
Longitudinal studies, which follow individuals over time, provide valuable insights into the long-term effects of media violence. These studies have shown that early habitual exposure to media violence in middle childhood predicts increased aggressiveness years later in adulthood, even when controlling for early aggressiveness. This suggests that the effects of media violence can persist over time and have lasting consequences for behavior.
4. How Can Parents And Educators Minimize The Negative Impact Of Televised Aggression?
Parents and educators can minimize the negative impact of televised aggression by monitoring media consumption, promoting critical viewing habits, and encouraging alternative activities. This multifaceted approach, discussed further at monstertelevision.com, can help children develop healthy attitudes towards violence and reduce the risk of aggressive behavior. By actively engaging in their children’s media experiences, parents and educators can create a safer and more nurturing environment.
4.1 What Strategies Can Parents Employ To Monitor Media Consumption?
Parents can employ several strategies to monitor media consumption effectively. One approach is to set clear limits on screen time, ensuring that children engage in a variety of activities. Another strategy is to co-view media with children, allowing parents to discuss the content and provide context. Parents can also use parental control tools to block access to inappropriate content and monitor what their children are watching.
4.2 How Can Critical Viewing Habits Be Promoted In Children?
Critical viewing habits can be promoted by encouraging children to question the messages portrayed in media. Parents and educators can discuss the motivations behind violent acts, the consequences of violence, and the potential biases in media representations. By teaching children to think critically about what they are watching, they can become more discerning consumers of media and less likely to be influenced by its negative effects.
4.3 What Alternative Activities Can Be Encouraged To Reduce Media Consumption?
Alternative activities can include outdoor play, sports, hobbies, reading, and creative pursuits. Encouraging children to engage in these activities can reduce their reliance on media for entertainment and provide opportunities for social interaction, physical activity, and cognitive development. By offering a variety of alternatives, parents and educators can help children develop well-rounded interests and reduce their exposure to violent media.
4.4 Is There A Role For Media Literacy Programs In Schools?
Yes, media literacy programs in schools can play a crucial role in educating children about the effects of media violence. These programs can teach children how to critically analyze media messages, understand the techniques used to create violent content, and develop strategies for resisting negative influences. By incorporating media literacy into the curriculum, schools can empower children to make informed choices about their media consumption.
4.5 How Effective Are Ratings And Warning Labels On Media Content?
Ratings and warning labels on media content can be helpful tools for parents, but they are not always effective on their own. Parents need to be aware of the rating system and understand what the different ratings mean. However, ratings can be subjective and may not always accurately reflect the content of the media. Parents should also consider their own values and beliefs when making decisions about what media is appropriate for their children.
4.6 Can Family Discussions About Media Violence Help Mitigate Its Effects?
Yes, family discussions about media violence can be highly effective in mitigating its effects. These discussions provide opportunities for parents to share their values, address concerns, and help children process the messages they are receiving from media. By creating an open and supportive environment for discussing media violence, parents can help children develop healthy attitudes and behaviors.
5. Does Media Violence Cause Both Short-Term and Long-Term Effects?
Yes, research indicates that media violence causes both short-term and long-term effects on aggression. Short-term effects include priming, arousal, and mimicry, while long-term effects include observational learning and desensitization. These processes can lead to an increased risk of aggressive behavior over time. It’s important to understand these effects to develop strategies for mitigating the potential harm.
5.1 How Do Short-Term Effects Manifest After Exposure To Media Violence?
Short-term effects typically manifest as increased aggressive thoughts, feelings, and behaviors immediately after exposure to media violence. For example, individuals may be more likely to engage in aggressive acts, express hostile emotions, or have aggressive thoughts. These effects are often temporary but can still have significant consequences, especially in situations where aggression is likely to occur.
5.2 What Are Some Examples Of Long-Term Effects Resulting From Exposure To Media Violence?
Long-term effects can include the development of aggressive personality traits, a greater acceptance of violence, and a desensitization to the suffering of others. Individuals who are repeatedly exposed to media violence may become more likely to engage in aggressive behavior in their daily lives, have difficulty empathizing with others, and view violence as a normal or acceptable way to resolve conflicts. These effects can have lasting consequences for individuals and society.
5.3 Is There A Link Between Childhood Exposure To Media Violence And Adult Aggression?
Yes, longitudinal studies have shown a clear link between childhood exposure to media violence and adult aggression. Children who are repeatedly exposed to media violence are more likely to exhibit aggressive behaviors as adults, even when controlling for other factors such as socioeconomic status and family environment. This suggests that the effects of media violence can persist over time and have a lasting impact on behavior.
5.4 Do All Children Respond The Same Way To Media Violence?
No, not all children respond the same way to media violence. Individual differences in personality, temperament, and social environment can influence the impact of media violence. Some children may be more vulnerable to the negative effects of media violence, while others may be more resilient. Factors such as parental involvement, peer influence, and media literacy skills can also play a role in moderating the effects of media violence.
5.5 How Can Early Intervention Programs Help Reduce The Risk Of Long-Term Effects?
Early intervention programs can help reduce the risk of long-term effects by addressing the underlying factors that contribute to aggression. These programs may focus on teaching children conflict resolution skills, promoting empathy, and providing support for families. By intervening early in a child’s life, it is possible to prevent the development of aggressive behavior patterns and promote healthy social and emotional development.
5.6 What Role Does The Media Industry Play In Addressing The Issue Of Media Violence?
The media industry has a responsibility to address the issue of media violence by creating content that is less violent, providing accurate ratings and warning labels, and supporting research on the effects of media violence. The industry can also play a role in promoting media literacy and educating consumers about the potential risks of media violence. By working collaboratively with researchers, educators, and parents, the media industry can help create a safer and more responsible media environment.
6. Are There Specific Characteristics Of Violent Media That Increase Its Impact?
Yes, specific characteristics of violent media can increase its impact on viewers, particularly on children. These characteristics include portrayals of violence as justified, rewards for violent behavior, and identification with the perpetrator of violence. Understanding these factors, discussed further at monstertelevision.com, can help parents and educators make informed decisions about media consumption.
6.1 How Does Justification Of Violence Affect Viewers?
Portraying violence as justified can increase its impact on viewers by making it seem more acceptable or even necessary. When violence is presented as a legitimate response to a perceived threat or injustice, viewers may be more likely to condone or imitate it. This can normalize violence and reduce inhibitions against aggressive behavior.
6.2 Why Is Showing Rewards For Violence Problematic?
Showing rewards for violence can reinforce the idea that violence is an effective way to achieve goals. When characters are rewarded for engaging in violent behavior, viewers may learn that violence is a successful strategy for getting what they want. This can increase the likelihood of aggressive behavior, especially in situations where individuals believe that violence will lead to positive outcomes.
6.3 How Does Identification With The Perpetrator Influence Behavior?
When viewers identify with the perpetrator of violence, they are more likely to imitate the perpetrator’s behavior. Identification can occur when viewers admire, respect, or feel a sense of connection to the perpetrator. This can lead to viewers internalizing the perpetrator’s values and beliefs, including the acceptance of violence as a means of resolving conflicts.
6.4 What Impact Does Realistic Violence Have On Viewers?
Realistic violence, which closely mimics real-world violence, can have a greater impact on viewers than stylized or cartoonish violence. Realistic violence may be more disturbing and emotionally arousing, leading to increased anxiety, fear, and aggression. It can also desensitize viewers to the suffering of others and make them more accepting of violence in real life.
6.5 Does Humor In Violent Media Mitigate Or Exacerbate Its Effects?
The effect of humor in violent media is complex and may depend on the context and the individual viewer. Some research suggests that humor can mitigate the effects of violence by reducing its emotional impact. However, other research suggests that humor can exacerbate the effects of violence by normalizing it and making it seem less serious.
6.6 How Does The Age Of The Viewer Impact The Effect Of These Characteristics?
The age of the viewer can significantly impact the effect of these characteristics. Younger children may be more vulnerable to the negative effects of violent media because they have less developed critical thinking skills and are more likely to imitate what they see. Older children and adults may be better able to critically analyze violent media and resist its negative influences.
7. Are There Specific Groups More Susceptible To The Negative Effects Of Media Violence?
While anyone can be affected by media violence, certain groups, such as children with pre-existing aggressive tendencies or those lacking strong parental guidance, may be more susceptible to its negative effects. Understanding these vulnerabilities, explored further at monstertelevision.com, can help tailor interventions and support to those most at risk.
7.1 Do Children With Pre-Existing Aggressive Tendencies React Differently?
Yes, children with pre-existing aggressive tendencies may react differently to media violence. These children may be more likely to identify with the perpetrators of violence, imitate violent behavior, and have difficulty controlling their impulses. Media violence can exacerbate their existing aggressive tendencies and increase the likelihood of engaging in violent behavior.
7.2 What Role Does Parental Guidance Play In Mitigating These Effects?
Parental guidance plays a crucial role in mitigating the effects of media violence. Parents who actively monitor their children’s media consumption, discuss media content with their children, and provide clear guidelines about acceptable behavior can help reduce the negative impact of media violence. Parental guidance can also help children develop critical thinking skills and resist the negative influences of violent media.
7.3 How Does Socioeconomic Status Affect Susceptibility?
Socioeconomic status can affect susceptibility to media violence by influencing access to resources and opportunities. Children from low-income families may be more likely to live in violent neighborhoods, have limited access to positive role models, and experience high levels of stress. These factors can increase their vulnerability to the negative effects of media violence.
7.4 What Impact Does Peer Influence Have On Media Violence Effects?
Peer influence can have a significant impact on media violence effects. Children who associate with peers who endorse violence may be more likely to be influenced by violent media. Peer pressure can also lead children to engage in risky behaviors, such as watching violent media with their friends, even if they know it is not appropriate.
7.5 Are There Gender Differences In How Media Violence Affects Individuals?
Research on gender differences in how media violence affects individuals is mixed. Some studies suggest that males may be more likely to exhibit aggressive behavior after exposure to violent media, while females may be more likely to experience anxiety and fear. However, other studies have found no significant gender differences. More research is needed to fully understand the role of gender in media violence effects.
7.6 Can The Viewing Environment Influence The Effects Of Media Violence?
Yes, the viewing environment can influence the effects of media violence. Children who watch violent media in unsupervised settings may be more likely to be negatively affected than those who watch with their parents or other responsible adults. The presence of others can provide opportunities for discussion, support, and guidance, which can help mitigate the negative effects of media violence.
8. What Are Some Strategies For Reducing Exposure To And The Effects Of Media Violence?
Strategies for reducing exposure to and the effects of media violence include setting media consumption limits, promoting alternative activities, teaching critical viewing skills, and engaging in open communication. These strategies, detailed further at monstertelevision.com, can help individuals and families develop healthy media habits and reduce the risk of aggression.
8.1 How Can Families Set Effective Media Consumption Limits?
Families can set effective media consumption limits by establishing clear rules about screen time, monitoring media content, and providing alternative activities. It is important to involve children in the process of setting limits and to explain the reasons behind the rules. Families can also use parental control tools to block access to inappropriate content and track media usage.
8.2 What Types Of Alternative Activities Can Be Encouraged?
A wide range of alternative activities can be encouraged, including outdoor play, sports, hobbies, reading, creative pursuits, and social interaction. These activities can provide opportunities for physical activity, cognitive development, and social and emotional growth. By offering a variety of alternatives, families can help children develop well-rounded interests and reduce their reliance on media for entertainment.
8.3 How Can Parents Teach Critical Viewing Skills To Their Children?
Parents can teach critical viewing skills by discussing media content with their children, asking questions about the messages being portrayed, and encouraging them to think critically about the motivations and consequences of violence. Parents can also help children identify stereotypes, biases, and other forms of media manipulation. By teaching critical viewing skills, parents can empower children to make informed choices about their media consumption.
8.4 Why Is Open Communication Important In Addressing Media Violence?
Open communication is essential for addressing media violence because it allows families to discuss their concerns, share their values, and provide support for one another. Open communication can also help children develop trust in their parents and feel comfortable sharing their thoughts and feelings. By creating a safe and supportive environment for discussing media violence, families can help children develop healthy attitudes and behaviors.
8.5 What Role Can Schools Play In Reducing Media Violence Effects?
Schools can play a crucial role in reducing media violence effects by incorporating media literacy into the curriculum, providing counseling and support services, and promoting positive social and emotional development. Schools can also work with families to develop strategies for reducing media violence exposure and promoting healthy media habits. By working collaboratively with families and communities, schools can help create a safer and more responsible media environment.
8.6 How Can Communities Support Efforts To Reduce Media Violence?
Communities can support efforts to reduce media violence by providing resources for families, promoting media literacy, and advocating for responsible media policies. Communities can also create opportunities for positive social interaction and recreational activities, which can help reduce reliance on media for entertainment. By working together, communities can help create a safer and more supportive environment for children and families.
9. How Does This Research Apply To Content Specifically Featuring Monsters?
The research on televised aggression is directly applicable to content featuring monsters, as the portrayal of violence, even in fantastical contexts, can still trigger the same psychological processes that lead to aggression. Whether it’s a zombie apocalypse, a vampire slaying spree, or a kaiju battle, the presence of violence can have a measurable impact, especially on vulnerable viewers. At monstertelevision.com, we encourage a balanced approach to enjoying monster content, one that acknowledges the potential risks and promotes responsible viewing habits.
9.1 Does Fictional Violence Still Have The Same Impact As Realistic Violence?
While fictional violence may not have the same immediate emotional impact as realistic violence, it can still contribute to long-term desensitization and the normalization of aggression. The key factors are the context in which the violence is presented, the extent to which viewers identify with the characters, and the frequency of exposure. Even fantastical violence can have a cumulative effect over time.
9.2 Are Certain Types Of Monsters More Problematic Than Others?
The potential harm of monster content is less about the type of monster and more about how violence is portrayed. Content that glorifies violence, presents it as justified, or lacks consequences for aggressive actions is more problematic. The more realistic the violence, the more likely it is to have an impact on viewers.
9.3 How Can Parents Approach Monster-Themed Content With Their Children?
Parents can approach monster-themed content with their children by watching together and discussing the themes, motivations, and consequences of violence. Encourage critical thinking by asking questions like, “Why did the monster do that?” or “Was there a better way to solve that problem?” It’s also important to emphasize the difference between fantasy and reality.
9.4 Is It Necessary To Completely Avoid Monster Television?
It is generally not necessary to completely avoid monster television. Many monster shows offer valuable storytelling, explore complex themes, and provide opportunities for creative expression. The key is to be mindful of the content, set appropriate boundaries, and engage in meaningful discussions about what you are watching.
9.5 What Resources Are Available For Responsible Monster Content Consumption?
There are resources available on monstertelevision.com, Common Sense Media, and other media literacy organizations that provide guidance on responsible monster content consumption. These resources offer reviews, ratings, and discussion guides to help parents and educators make informed decisions about what to watch.
9.6 What Are The Benefits Of Exploring Monsters In Media?
Despite the potential risks, exploring monsters in media can offer numerous benefits. Monster stories often reflect societal fears and anxieties, allowing us to confront these issues in a safe and imaginative space. They can also promote empathy by exploring the humanity within monsters and the monstrosity within humans.
10. What Are The Key Takeaways From This Research, And How Can They Be Applied In Daily Life?
The key takeaway is that exposure to televised aggression, even in fantastical contexts, can have both short-term and long-term effects on behavior, particularly in vulnerable individuals. By being mindful of media consumption, promoting critical viewing habits, and engaging in open communication, we can mitigate these risks and enjoy monster television responsibly. Remember, monstertelevision.com is here to provide the information and community you need to navigate this complex landscape.
10.1 How Can Individuals Become More Mindful Of Their Own Media Consumption?
Individuals can become more mindful of their own media consumption by tracking how much time they spend watching television, playing video games, and using social media. They can also reflect on the types of content they are consuming and consider how it might be affecting their thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. Setting limits and prioritizing other activities can also help.
10.2 What Questions Should Be Asked When Critically Viewing Media?
When critically viewing media, individuals should ask questions such as: What is the message being conveyed? Who created this content, and what are their motivations? How might this content affect my thoughts, feelings, and behaviors? Is there a different way to interpret this content?
10.3 How Can Communication About Media Violence Be Initiated With Children?
Communication about media violence can be initiated with children by asking them about what they are watching, listening to their perspectives, and sharing your own thoughts and feelings. It’s important to create a safe and supportive environment where children feel comfortable asking questions and expressing their concerns.
10.4 What Are The Long-Term Benefits Of Promoting Responsible Media Consumption?
The long-term benefits of promoting responsible media consumption include reduced aggression, increased empathy, improved critical thinking skills, and healthier social and emotional development. By fostering responsible media habits, we can create a more positive and supportive environment for ourselves and future generations.
10.5 How Can Community Organizations Help Promote Media Literacy?
Community organizations can help promote media literacy by offering workshops, seminars, and educational programs for individuals and families. They can also provide resources and support for schools and other community institutions. By working collaboratively, community organizations can help raise awareness about the effects of media violence and promote responsible media consumption.
10.6 What Are Some Future Directions For Research On Media Violence?
Future directions for research on media violence include exploring the effects of new media technologies, examining the role of individual differences in media violence effects, and developing more effective interventions for reducing media violence exposure and its consequences. Continued research is essential for staying ahead of the curve and addressing the evolving challenges of media violence in the digital age.
Join us at monstertelevision.com to explore these topics in greater detail and connect with a community of fellow monster enthusiasts. Discover in-depth reviews, breaking news, behind-the-scenes insights, and a forum for discussing your favorite shows. Our commitment is to provide a balanced and informative perspective on the world of monster television, ensuring you can enjoy your favorite content responsibly. Don’t miss out – visit monstertelevision.com today!
 A scene from a monster-themed television show showcasing the intensity and drama inherent in monster media
A scene from a monster-themed television show showcasing the intensity and drama inherent in monster media
Address: 900 S Broadway, Los Angeles, CA 90015, United States
Phone: +1 (213) 740-2700
Website: monstertelevision.com
FAQ’s
1. Is All Violence On TV Harmful?
Not necessarily. The impact of violence depends on context, justification, and consequences.
2. Are Video Games More Harmful Than TV?
Some studies suggest video games can be more impactful due to active participation.
3. Can Cartoons Desensitize Children?
Yes, repeated exposure can lead to desensitization over time.
4. How Can I Talk To My Child About A Scary Show?
Discuss the difference between fantasy and reality, and address any fears.
5. Does Media Violence Always Lead To Real-World Aggression?
No, but it’s a risk factor that can contribute to aggressive behavior.
6. How Do Media Ratings Help Parents?
They offer guidance, but parental involvement is crucial.
7. What Is A “Media Diet”?
Consciously managing your media consumption for better well-being.
8. Does A Child’s Personality Affect Their Susceptibility?
Yes, children with pre-existing tendencies may be more affected.
9. How Can Schools Teach Media Literacy?
By including critical viewing and analytical skills in the curriculum.
10. Where Can I Find Responsible Monster Content?
Visit monstertelevision.com for curated reviews and community discussions.
