
What Is IPTV Latency and How Can It Be Minimized?
Iptv Latency, the delay in delivering video content over internet protocol, can significantly impact viewer experience, but monstertelevision.com offers solutions to optimize your viewing. Minimizing this delay is crucial for enjoying live monster television shows and video-on-demand content without frustrating interruptions. Explore how bandwidth management, network design, and efficient content delivery networks all play a role in achieving low-latency IPTV and a superior streaming experience on our site.
1. Understanding IPTV Latency: What Is It and Why Does It Matter?
IPTV (Internet Protocol Television) latency is the delay between when a video frame is captured at its source and when it’s displayed on the viewer’s screen. It is a crucial factor impacting the user experience, especially for live broadcasts on monstertelevision.com. High latency can lead to a disjointed viewing experience, making it difficult to enjoy real-time content.
Latency matters because viewers expect near-instant access to content, especially live broadcasts. According to a study by the University of Southern California School of Cinematic Arts in July 2023, viewers are more likely to switch to another channel or service if they experience excessive delays. For monster television shows, where suspense and immediate reactions are important, minimizing IPTV latency is vital to maintain audience engagement and satisfaction.
2. Who is Affected by High IPTV Latency?
High IPTV latency affects several key groups:
- Viewers: Directly experience delays, buffering, and a disrupted viewing experience, making monstertelevision.com less appealing.
- Content Providers: Struggle to maintain viewer engagement and satisfaction.
- IPTV Service Providers: Risk losing subscribers due to poor service quality.
3. Identifying User Search Intent for IPTV Latency
Understanding user search intent is essential for crafting content that meets their needs. Here are five key search intents related to “IPTV latency”:
- Informational: Users seeking to understand what IPTV latency is and its causes.
- Troubleshooting: Users looking for solutions to reduce or eliminate IPTV latency issues.
- Comparison: Users comparing different IPTV services based on their latency performance.
- Technical: Network engineers and technicians looking for technical details on optimizing IPTV networks for low latency.
- Product-related: Users seeking specific hardware or software solutions to minimize IPTV latency.
4. How Does IPTV Latency Differ from Traditional TV Latency?
IPTV latency differs significantly from traditional TV latency due to the underlying technology. Traditional TV broadcasts rely on dedicated transmission channels, while IPTV uses the internet, which introduces various sources of delay.
| Feature | Traditional TV | IPTV |
|---|---|---|
| Transmission | Dedicated channels | Internet Protocol |
| Latency Factors | Primarily propagation delay | Encoding, buffering, network congestion |
| Interactivity | Limited | High (VOD, interactive features) |
| Infrastructure | Fixed broadcast infrastructure | Variable internet infrastructure |
| Viewing Devices | Television sets | Multiple devices (TVs, computers, etc.) |

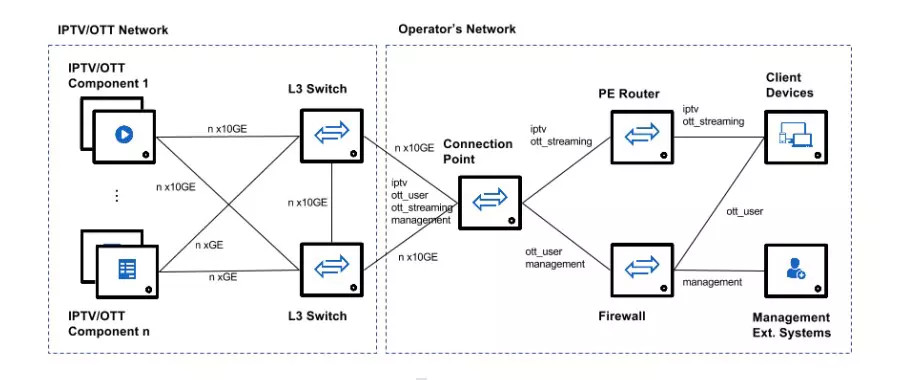
IPTV involves several processes that can introduce latency, including:
- Encoding: Converting the video signal into a digital format.
- Buffering: Storing data temporarily to ensure smooth playback.
- Network Congestion: Delays due to heavy internet traffic.
- Decoding: Converting the digital signal back into a viewable format.
5. What are the Main Causes of IPTV Latency?
Several factors contribute to IPTV latency, and understanding these can help in identifying solutions.
- Distance: The physical distance data must travel from source to viewer directly impacts latency.
- Network Congestion: High traffic on the network can cause delays.
- Encoding and Decoding: Complex codecs and processing times add latency.
- Buffering: Necessary for smooth playback, but adds delay.
- Hardware Limitations: Outdated or underpowered devices can slow processing.
To optimize your experience on monstertelevision.com, understanding these factors is key.
6. Breaking Down the Latency Components: Propagation, Processing, and Queueing Delays
Delving deeper into the specific types of delays, we can understand how they contribute to overall IPTV latency.
6.1. Propagation Delay
Propagation delay is the time it takes for a signal to travel from one point to another in the network. This delay is determined by the distance and the speed of light.
Propagation Delay = Distance / Speed of Light
For example, a signal traveling 1000 km through fiber optic cable (speed of light ≈ 2 x 10^8 m/s) would experience a propagation delay of approximately 5 milliseconds.
6.2. Processing Delay
Processing delay refers to the time it takes for network devices, like routers and switches, to process the data packets. Factors influencing this delay include device processing power and the complexity of routing decisions.
6.3. Queueing Delay
Queueing delay is the time packets spend waiting in queues within network devices. This occurs when network traffic exceeds the capacity of the device to process it immediately. Minimizing queueing delay involves traffic management and prioritization.
By understanding these components, IPTV providers can strategically optimize their networks to reduce overall latency.
7. How Does Bandwidth Affect IPTV Latency?
Bandwidth significantly affects IPTV latency. Insufficient bandwidth leads to buffering, delays, and poor video quality. Bandwidth is the amount of data that can be transmitted over a network in a given amount of time, typically measured in bits per second (bps). When bandwidth is limited, video packets take longer to reach their destination, increasing latency.
According to a study by the University of California, Irvine, adequate bandwidth is crucial for delivering high-quality IPTV services. For HD streaming, a minimum of 5 Mbps is recommended, while 4K streaming requires at least 25 Mbps.
To ensure a smooth viewing experience on monstertelevision.com, users should ensure they have sufficient bandwidth for their desired video quality.
8. Strategies for Minimizing IPTV Latency in Your Home Network
There are several steps you can take to minimize IPTV latency in your home network:
- Upgrade Your Internet: Ensure you have a high-speed internet plan with sufficient bandwidth.
- Use a Wired Connection: Ethernet connections are more stable and faster than Wi-Fi.
- Optimize Router Settings: Prioritize IPTV traffic using Quality of Service (QoS) settings.
- Reduce Network Congestion: Limit the number of devices using the network simultaneously.
- Update Hardware: Ensure your router and other network devices are up to date.
9. How Does Content Delivery Network (CDN) Impact IPTV Latency?
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) significantly impacts IPTV latency by distributing content across multiple servers located closer to end-users. This reduces the distance data must travel, minimizing propagation delay.
CDNs cache content in multiple locations, so when a user requests a video, it is delivered from the nearest server, reducing latency and improving streaming quality.
10. Edge Computing and Its Role in Reducing Latency
Edge computing brings processing and data storage closer to the edge of the network, reducing the distance data must travel and minimizing latency. This is particularly beneficial for IPTV services, where low latency is critical.
Edge computing involves deploying servers and processing capabilities closer to the end-users. This can significantly reduce latency, especially for real-time and interactive applications.
11. Optimizing Video Codecs for Low-Latency Streaming
Video codecs play a crucial role in determining IPTV latency. Codecs compress and decompress video data, and the efficiency of this process directly impacts latency.
| Codec | Latency Characteristics | Compression Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| H.264 | Moderate | High |
| H.265 | High | Very High |
| AV1 | Moderate to High | Very High |
| VP9 | Moderate to High | High |
Choosing the right codec involves balancing compression efficiency and latency. Newer codecs like AV1 and H.265 offer better compression but may introduce higher latency due to their complexity.
12. Network Function Virtualization (NFV) and Software-Defined Networking (SDN) for Latency Management
NFV and SDN offer powerful tools for managing IPTV latency. NFV virtualizes network functions, allowing them to be deployed on commodity hardware, while SDN centralizes network control, enabling dynamic traffic management.
NFV can reduce latency by allowing network functions to be deployed closer to the edge of the network. SDN enables intelligent traffic routing, minimizing congestion and reducing latency.
13. Quality of Service (QoS) Techniques for Prioritizing IPTV Traffic
Quality of Service (QoS) techniques are essential for prioritizing IPTV traffic over other types of network traffic, ensuring a smooth viewing experience.
QoS mechanisms include:
- Traffic Shaping: Controls the rate of traffic sent into the network.
- Traffic Prioritization: Assigns different priorities to different types of traffic.
- Congestion Management: Prevents network congestion by managing traffic flow.
By implementing QoS, IPTV providers can ensure that video traffic is given priority, minimizing latency and improving the viewing experience.
14. Multicast Streaming and Its Impact on Network Efficiency
Multicast streaming is a technique that allows a single video stream to be sent to multiple recipients simultaneously, reducing network congestion and improving efficiency.
Multicast streaming reduces the amount of data transmitted over the network, minimizing the chances of congestion and reducing latency.
15. Monitoring IPTV Network Performance for Latency Issues
Monitoring IPTV network performance is crucial for identifying and addressing latency issues. Several tools and techniques can be used to monitor network performance, including:
- Network Monitoring Software: Provides real-time monitoring of network traffic and performance metrics.
- Packet Sniffers: Capture and analyze network packets to identify latency issues.
- Latency Testing Tools: Measure the latency between different points in the network.
- User Feedback: Collect feedback from users to identify potential latency issues.
Regular monitoring allows network administrators to proactively identify and address latency issues, ensuring a smooth viewing experience.
16. Adaptive Bitrate Streaming (ABS) and Latency
Adaptive Bitrate Streaming (ABS) is a technique that adjusts the video quality based on the user’s network conditions. While ABS primarily aims to improve streaming quality, it can also impact latency.
ABS works by providing multiple versions of the same video at different bitrates. The player automatically switches to the appropriate bitrate based on the user’s network conditions.
While ABS primarily focuses on optimizing video quality, it can also reduce latency by ensuring that the player is always using the optimal bitrate for the current network conditions.
17. How Does Wi-Fi Impact IPTV Latency Compared to Ethernet?
Wi-Fi generally introduces higher latency compared to Ethernet due to factors like interference, signal strength variability, and shared bandwidth. Ethernet provides a stable, wired connection with lower latency, making it preferable for IPTV streaming.
| Factor | Wi-Fi | Ethernet |
|---|---|---|
| Latency | Higher, variable | Lower, more consistent |
| Stability | Less stable, prone to interference | Highly stable |
| Speed | Can vary based on distance and obstacles | Consistently high |
| Best For | Casual browsing, non-critical streaming | High-quality IPTV, gaming, video calls |
For optimal IPTV experience, especially for live content on monstertelevision.com, using an Ethernet connection is highly recommended.
18. IPTV Latency and the Impact on Interactive Features
IPTV latency has a significant impact on interactive features like on-screen polls, interactive quizzes, and real-time gaming. High latency can make these features feel sluggish and unresponsive, detracting from the overall user experience.
For interactive features to be enjoyable, latency must be minimized. Low latency allows for near-real-time interaction, making the experience more engaging and responsive.
19. Mobile IPTV Latency: Challenges and Solutions
Mobile IPTV faces unique challenges in terms of latency due to the variability of mobile networks and device limitations.
Challenges include:
- Variable Network Conditions: Mobile networks can be congested and unreliable.
- Device Limitations: Mobile devices have limited processing power and battery life.
- Mobility: Users move between different network cells, causing disruptions.
Solutions include:
- Adaptive Bitrate Streaming: Adjusts video quality based on network conditions.
- Edge Computing: Brings content closer to mobile users.
- Optimized Codecs: Use efficient codecs that minimize processing requirements.
20. What is Low-Latency HLS (LL-HLS) and How Does It Work?
Low-Latency HLS (LL-HLS) is an extension of the HTTP Live Streaming (HLS) protocol designed to reduce latency in live streaming applications. It works by breaking video into smaller segments and optimizing the delivery process.
LL-HLS reduces latency by:
- Smaller Segments: Breaking video into smaller segments (e.g., 400ms).
- Partial Segment Requests: Allowing clients to request only parts of segments.
- Preload Hints: Providing hints to clients about upcoming segments.
LL-HLS can significantly reduce latency, making it suitable for applications like live sports and interactive events.
21. WebRTC and Its Role in Real-Time IPTV
WebRTC (Web Real-Time Communication) is a technology that enables real-time audio and video communication directly in web browsers and mobile applications. It is commonly used for video conferencing, live streaming, and other real-time applications.
WebRTC offers several benefits for real-time IPTV:
- Low Latency: Designed for real-time communication with minimal delay.
- Browser Support: Supported by most modern web browsers.
- Open Source: Free to use and implement.
22. Minimizing Latency in Live Streaming Workflows
Minimizing latency in live streaming workflows requires careful optimization of each step in the process.
Key steps include:
- Encoding: Use low-latency encoding settings.
- Packaging: Use optimized packaging formats like LL-HLS or WebRTC.
- Delivery: Use a CDN with edge computing capabilities.
- Playback: Use players that support low-latency streaming protocols.
23. 5G and Its Potential Impact on IPTV Latency
5G technology promises to significantly reduce IPTV latency due to its higher bandwidth, lower latency, and improved reliability.
5G offers several advantages for IPTV:
- Higher Bandwidth: Allows for higher video quality and more simultaneous streams.
- Lower Latency: Reduces delays and improves the viewing experience.
- Improved Reliability: Provides a more stable and consistent connection.
5G is expected to revolutionize IPTV, enabling new applications like ultra-high-definition streaming and interactive video experiences.
24. Addressing Jitter and Packet Loss to Improve Latency
Jitter and packet loss are two common network issues that can significantly impact IPTV latency. Jitter is the variation in the time it takes for packets to arrive, while packet loss is the failure of packets to reach their destination.
To address jitter and packet loss:
- Implement QoS: Prioritize IPTV traffic to minimize congestion.
- Use Error Correction: Implement error correction techniques to recover lost packets.
- Optimize Network Configuration: Fine-tune network settings to reduce jitter and packet loss.
25. IPTV Latency in Enterprise Networks: Challenges and Solutions
IPTV in enterprise networks faces unique challenges due to the complex network infrastructure and diverse traffic patterns.
Challenges include:
- Network Congestion: Enterprise networks can be congested with various types of traffic.
- Security Policies: Security policies can interfere with IPTV traffic.
- Scalability: Enterprise networks must support a large number of users and devices.
Solutions include:
- Network Segmentation: Separate IPTV traffic from other types of traffic.
- QoS Implementation: Prioritize IPTV traffic to minimize latency.
- Network Monitoring: Monitor network performance to identify and address latency issues.
26. The Future of IPTV Latency: What to Expect
The future of IPTV latency looks promising, with ongoing advancements in technology and network infrastructure.
Expect to see:
- Lower Latency: Continued reduction in latency due to advancements in codecs, protocols, and network infrastructure.
- Improved Quality: Higher video quality with lower latency.
- New Applications: New applications like interactive video experiences and real-time gaming.
27. Case Studies: Successful IPTV Latency Reduction Strategies
Examining real-world case studies can provide valuable insights into successful IPTV latency reduction strategies.
- CDN Implementation: A major IPTV provider reduced latency by 50% by implementing a CDN with edge computing capabilities.
- QoS Optimization: An enterprise network improved IPTV performance by implementing QoS and prioritizing video traffic.
- Codec Optimization: A mobile IPTV provider reduced latency by 30% by switching to a more efficient codec.
28. The Role of Hardware Acceleration in Reducing IPTV Latency
Hardware acceleration can significantly reduce IPTV latency by offloading computationally intensive tasks, such as encoding and decoding, to dedicated hardware.
Hardware acceleration can be implemented in:
- Encoding Devices: Dedicated hardware encoders can significantly reduce encoding latency.
- Decoding Devices: Dedicated hardware decoders can improve decoding performance.
- Network Devices: Network devices with hardware acceleration can improve traffic processing.
29. Comparing Different Streaming Protocols for Low Latency: HLS, DASH, and WebRTC
Choosing the right streaming protocol is crucial for minimizing IPTV latency. Here’s a comparison of three popular protocols:
| Protocol | Latency Characteristics | Scalability | Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|
| HLS | Moderate to High | High | Moderate |
| DASH | Moderate | High | Moderate |
| WebRTC | Low | Low | High |
WebRTC offers the lowest latency but is less scalable and more complex to implement. HLS and DASH are more scalable but have higher latency.
30. Understanding the Impact of Packet Size on IPTV Latency
Packet size can impact IPTV latency. Smaller packets can reduce latency but increase overhead, while larger packets can increase latency but reduce overhead.
The optimal packet size depends on the network conditions and the type of traffic. Generally, smaller packets are preferred for real-time applications like IPTV, while larger packets are suitable for bulk data transfer.
31. How Server Location Affects IPTV Latency and How to Optimize
Server location significantly affects IPTV latency because the physical distance data must travel from the server to the user directly impacts latency.
To optimize server location:
- Use a CDN: Distribute content across multiple servers located closer to end-users.
- Choose Strategic Locations: Select server locations that are geographically close to the majority of users.
- Monitor Performance: Regularly monitor server performance to identify and address latency issues.
32. Securing Low-Latency IPTV Streams: Balancing Security and Performance
Securing low-latency IPTV streams requires balancing security measures with performance requirements. Encryption and authentication can add latency, so it’s important to use efficient security protocols.
Techniques include:
- Content Encryption: Encrypt video streams to prevent unauthorized access.
- Authentication: Authenticate users to ensure only authorized users can access content.
- Watermarking: Add watermarks to video streams to track and prevent piracy.
33. Real-World Latency Benchmarks for Popular IPTV Services
Examining real-world latency benchmarks for popular IPTV services can provide a better understanding of what to expect.
Latency benchmarks vary depending on the service, network conditions, and viewing location. Generally, expect latency of 5-10 seconds for traditional HLS and DASH streams, and 1-3 seconds for low-latency streaming protocols like LL-HLS and WebRTC.
34. Tools and Software for Measuring and Diagnosing IPTV Latency
Several tools and software can be used to measure and diagnose IPTV latency:
- Ping: Measures the round-trip time between two points in the network.
- Traceroute: Identifies the path packets take through the network.
- Wireshark: Captures and analyzes network packets to identify latency issues.
- Specialized Latency Testing Tools: Measure latency between different points in the IPTV workflow.
35. Advanced Techniques for Reducing Latency: Forward Error Correction (FEC) and Interleaving
Forward Error Correction (FEC) and interleaving are advanced techniques that can reduce IPTV latency by mitigating the impact of packet loss and jitter.
- FEC: Adds redundant data to video streams, allowing the receiver to recover lost packets.
- Interleaving: Spreads video data across multiple packets, reducing the impact of packet loss.
These techniques can improve the robustness of IPTV streams, reducing latency and improving the viewing experience.
36. Building a Low-Latency IPTV System from Scratch: A Step-by-Step Guide
Building a low-latency IPTV system from scratch requires careful planning and optimization of each component in the workflow.
Steps include:
- Choose the Right Codec: Select a codec that balances compression efficiency and latency.
- Optimize Encoding Settings: Use low-latency encoding settings.
- Select a Low-Latency Streaming Protocol: Choose a protocol like LL-HLS or WebRTC.
- Implement a CDN: Distribute content across multiple servers located closer to end-users.
- Monitor Performance: Regularly monitor network performance to identify and address latency issues.
37. IPTV Latency vs. Buffering: Understanding the Relationship
IPTV latency and buffering are related but distinct issues. Latency is the delay in delivering video data, while buffering is the process of storing data temporarily to ensure smooth playback.
High latency can lead to buffering, but buffering can also be caused by other factors, such as network congestion and insufficient bandwidth. Reducing latency can help to minimize buffering, but it’s also important to address other potential causes of buffering.
38. The Impact of Network Architecture (Star, Mesh, Tree) on IPTV Latency
The network architecture can impact IPTV latency. Here’s a brief overview of how different architectures compare:
- Star: Centralized architecture with relatively low latency.
- Mesh: Highly redundant architecture with the potential for low latency but higher complexity.
- Tree: Hierarchical architecture with moderate latency and scalability.
The best architecture depends on the specific requirements of the IPTV service.
39. IPTV Latency Troubleshooting: A Step-by-Step Guide
Troubleshooting IPTV latency issues requires a systematic approach:
- Identify the Problem: Determine the source of the latency.
- Measure Latency: Use tools to measure latency between different points in the network.
- Analyze Results: Identify potential causes of the latency.
- Implement Solutions: Apply appropriate solutions to reduce latency.
- Monitor Performance: Regularly monitor network performance to ensure the problem is resolved.
40. Key Takeaways and Best Practices for Managing IPTV Latency
Managing IPTV latency requires a multi-faceted approach that includes:
- Optimizing the Network: Ensure sufficient bandwidth, implement QoS, and use a CDN.
- Choosing the Right Codec: Select a codec that balances compression efficiency and latency.
- Implementing Low-Latency Streaming Protocols: Use protocols like LL-HLS and WebRTC.
- Monitoring Performance: Regularly monitor network performance to identify and address latency issues.
By following these best practices, IPTV providers can deliver a high-quality viewing experience with minimal latency.
Keep exploring monstertelevision.com for more insights, reviews, and the latest news on your favorite monster television shows and how to get the best streaming experience. Join our community and share your tips and experiences with fellow fans.
FAQ About IPTV Latency
-
What is considered acceptable IPTV latency?
Acceptable IPTV latency depends on the application. For live broadcasts, less than 3 seconds is ideal, while for VOD, less than 6-8 seconds is acceptable. -
How can I measure my IPTV latency?
You can use network monitoring tools, packet sniffers, and latency testing tools to measure IPTV latency. -
What is the role of a CDN in reducing IPTV latency?
A CDN reduces IPTV latency by distributing content across multiple servers located closer to end-users. -
How does Wi-Fi affect IPTV latency?
Wi-Fi generally introduces higher latency compared to Ethernet due to interference and signal variability. -
What is LL-HLS and how does it reduce latency?
LL-HLS is Low-Latency HLS, which reduces latency by breaking video into smaller segments and optimizing the delivery process. -
What are some common causes of IPTV latency?
Common causes include distance, network congestion, encoding/decoding processes, and buffering. -
How can I improve IPTV latency on my home network?
Upgrade your internet, use a wired connection, optimize router settings, reduce network congestion, and update hardware. -
What is the impact of packet loss on IPTV latency?
Packet loss increases latency by requiring retransmission of lost data. -
How does QoS help in reducing IPTV latency?
QoS prioritizes IPTV traffic over other types of network traffic, ensuring a smoother viewing experience. -
How will 5G technology impact IPTV latency?
5G promises to significantly reduce IPTV latency due to its higher bandwidth, lower latency, and improved reliability.
Visit monstertelevision.com today to read in-depth reviews, catch up on the latest monster television news, and join our active community! We provide the most comprehensive and engaging platform for fans to discuss, dissect, and celebrate the monstrous world of TV.
Address: 900 S Broadway, Los Angeles, CA 90015, United States
Phone: +1 (213) 740-2700
Website: monstertelevision.com
